原文:A Developer’s Guide To LLMOps: MLOps for Operationalizing LLMs
Three Keys of Effective Large Language Model Operations 有效的大型语言模型操作的三个关键
This blog is co-authored by Aparna Dhinakaran
本博客由Aparna Dhinakaran共同撰写
Operationalizing machine learning models in production and monitoring them effectively has been an emerging topic in the past few years. Whenever a model starts to fail silently in a production environment, it is critical to have the right set-up to understand the issue and troubleshoot the model in a timely manner. The use of GPT-4 as a replacement for various traditional model tasks is growing daily. What many teams consider a model today, may just be a prompt-and-response pair in the future. As teams deploy large language models to production, the same challenges around performance and task measurement still exist. Hence, LLMOps is essential to scale large language models and deploy them to production effectively.
在过去几年中,在生产中操作机器学习模型并对其进行有效监控一直是一个新兴话题。每当模型在生产环境中开始以静默方式失败时,进行正确的设置以了解问题并及时对模型进行故障排除至关重要。使用 GPT-4 作为各种传统模型任务的替代品每天都在增长。许多团队今天认为的模型,可能只是未来的一对快速响应。随着团队将大型语言模型部署到生产环境,性能和任务度量方面的相同挑战仍然存在。因此,LLMOps 对于扩展大型语言模型并将其有效地部署到生产环境至关重要。
What Is LLMOps? 什么是LLMOps?
Large language model operations (LLMOps) is a discipline that combines several techniques – such as prompt engineering, deploying LLM agents, and LLM observability – to optimize language models for specific contexts and make sure they provide the expected output to users.
大型语言模型操作 (LLMOps) 是一门结合了多种技术(例如提示工程、部署 LLM 代理和 LLM 可观察性)的学科,以针对特定上下文优化语言模型并确保它们为用户提供预期的输出。
In this article, we cover each of the techniques in detail and talk about the best practices to maintain LLMs in production.
在本文中,我们将详细介绍每种技术,并讨论在生产中维护LLM的最佳实践。

Prompt Engineering 提示工程
The concept of prompts and responses started to gain popularity after the introduction of large language models. A prompt is simply the specific task a user provides to a language model, and the response is the output of the language model that accomplishes the task. For example, a user might provide a medical report from a recent diagnosis and ask ChatGPT to summarize the document. In this case, the medical document and the action to summarize would define the prompt and the summary itself would define the response.
在引入大型语言模型后,提示和回复的概念开始变得流行起来。提示(prompt)只是用户向语言模型提供的具体任务,而回复(response)则是语言模型产生的完成该任务的输出。例如,用户可能会提供最近诊断的医疗报告,并要求ChatGPT对该文档进行总结。在这种情况下,医疗文档及其总结的动作将定义提示,而总结本身将定义回复。
Prompt engineering can be simply defined as the ability to talk and receive information from an AI software like ChatGPT. The better you are at prompt engineering, the better you are at communicating with large language models in order to make them complete specific tasks. A carefully crafted prompt can guide the model towards producing the desired output, while a poorly crafted prompt may result in irrelevant or nonsensical results.
“提示工程”可以简单定义为与像ChatGPT这样的AI软件进行对话并接收信息的能力。您在提示工程方面的能力越强,您在与大型语言模型进行交流以完成特定任务方面就越好。精心设计的提示可以引导模型产生所期望的输出,而设计不良的提示可能导致无关或荒谬的结果。
What Are the Prevailing Approaches for Prompt Engineering?
目前主要的提示工程方法有哪些?
Common approaches to prompt engineering include few-shot prompting, instructor based prompting, chain of thought prompting, and automatic prompt generation. Let’s dive into each.
其中一些常见的提示工程方法包括少样本提示(few-shot prompting)、教师引导提示(instructor based prompting)、思路链提示(chain of thought prompting)和自动提示生成(automatic prompt generation)。让我们深入了解每个方法。
Few-Shot Prompting 少样本提示
Few-shot prompting is a prompt engineering technique where the user provides a few examples of the task that the large language model should perform as well as a description of the task. This is a very useful technique to use when you have specific examples of a task since the language model will significantly try to adapt to the example format while generating the response.
少样本提示(few-shot prompting)是一种提示工程技术,用户提供了任务的几个示例以及任务的描述,让大型语言模型执行该任务。当您拥有任务的具体示例时,这是一种非常有用的技术,因为语言模型在生成响应时会尽量适应示例的格式。通过少样本提示,语言模型可以更好地理解和执行特定任务。
Instructor-Based Prompting 教师引导提示
Instructor based prompting is based on instructing the large language model to act as a specific person while performing the desired task. For example, if you are trying to write a blog about a specific topic, an example prompt could start with “I want you to act like a genius writer on the topic of…”. With this way, the response would be optimized.
教师引导提示(instructor based prompting)是一种基于指导的提示工程方法,通过指示大型语言模型在执行所需任务时扮演特定的角色或人物。例如,如果您想要撰写关于特定主题的博客文章,一个示例提示可以以“我想让你扮演一个关于……的天才作家”开头。通过这种方式,生成的回复可以得到优化,与期望的角色和风格相匹配。使用教师引导提示,可以引导语言模型以特定的方式产生输出。
Chain of Thought Prompting / CoT Prompting 思路链提示/CoT提示
Chain of thought prompting (CoT prompting) is used to accomplish complex tasks where the user breaks down a specific task into smaller sub-tasks and instructs the language model to perform small tasks in an incremental order in order to get to the final desired outcome. You can combine CoT prompting with instructor-based and few-shot prompting to get the best results.
思路链提示(CoT prompting)用于完成复杂任务,用户将具体任务分解为较小的子任务,并指示语言模型按照递增顺序执行这些小任务以达到最终的期望结果。您可以将思路链提示与教师引导和少样本提示相结合,以获得最佳结果。通过使用思路链提示,可以引导语言模型按照逐步递进的方式生成输出,从而有效地完成复杂任务。
Automatic Prompt Generation 自动提示生成
Finally, large language models can also be leveraged to generate prompts for a specific task. The user simply describes the task that they want to accomplish within a few sentences and asks the language model to come up with different options. The user then searches for the best prompt and gets to choose the prompt that he or she is the most interested in.
最后,还可以利用大型语言模型来生成特定任务的提示。用户只需用几句话描述他们想完成的任务,并要求语言模型提供不同的选项。用户可以搜索最佳提示,并选择自己最感兴趣的提示。这种自动生成提示的方法可以帮助用户在任务执行过程中探索和选择最合适的提示。
Why Are Prompt Templates Important? 为什么提示模板很重要?
Other than prompt engineering, using prompt templates are crucial for deploying task-specific LLMs into production. Prompt templates can be defined as pre-amble texts that is placed right before a user’s prompt. By using prompt templates, LLM developers can standardize the output format and quality regardless of the simplicity of the prompt provided by the user. Prompt templates create a scalable and reproducible way to generate prompts and can contain instructions to a language model, few-shot examples or different chain of actions to be executed. Let’s look at an example:
除了提示工程,使用提示模板对于将面向特定任务的大型语言模型(LLM)部署到生产环境中至关重要。提示模板可以定义为位于用户提示之前的开场文本。通过使用提示模板,LLM开发人员可以无论用户提供的提示简单与否,都可以标准化输出格式和质量。提示模板创造了一种可扩展和可复制的方式来生成提示,并可以包含对语言模型的指令、少样本示例或要执行的不同操作链。让我们看一个例子:
prompt_template = """ I want you to act as a branding expert for new companies. You need to come up with names to certain tech startups. Here are some examples of good company names: - search engine, Google - social media, Facebook - video sharing, YouTube The name should be short, catchy and easy to remember. What is a good name for a company that makes {product}? """
The example above is a prompt that uses few-shot and instruction-based language to prepare a language model for a reproducible output. Using this template, we can deploy an LLM application that can generate unique names for different sets of products. All the user has to do is to enter the product type!
上面的例子是一个使用少样本和教师引导语言来为语言模型准备可复制的输出的提示模板。使用这个模板,我们可以部署一个LLM应用程序,可以为不同的产品集生成独特的名称。用户只需输入产品类型即可!
How Can Prompts Be Managed At Scale?
如何大规模管理提示?
Other than prompt engineering and prompt templates, it is important to consider prompt management within a production environment. Within your LLM application, you can have different prompt templates and user inputs running continuously and it is very important to store your prompts and control their workflow. Hence, the ability to swap out production prompts or iterate on prompts during application development should be considered. For example, based on user feedback, you might want to conduct some A/B testing with different prompt templates and track the performance of each prompt in real-time.
除了提示工程和提示模板之外,在生产环境中考虑提示管理也很重要。在您的LLM应用程序中,您可以连续运行不同的提示模板和用户输入,存储提示并控制其工作流程非常重要。因此,应考虑在应用程序开发期间换出生产提示或迭代提示的能力。例如,根据用户反馈,您可能希望使用不同的提示模板执行一些 A/B 测试,并实时跟踪每个提示的性能。
What are LLM Agents?
什么是LLM代理?
Apart from managing prompts effectively, developing specific LLM applications tailored to a particular context or task can prove to be a challenging endeavor. This typically involves collecting relevant data, utilizing various methods to process it, and tweaking the LLM to ensure that it can deliver optimal responses within your business context. Fortunately, there are several tools available that can help streamline the process and enable you to scale your applications more efficiently.
除了有效管理提示之外,针对特定上下文或任务开发定制的LLM应用程序可能是一项具有挑战性的工作。这通常涉及收集相关数据、使用各种方法进行处理,并调整LLM以确保在您的业务环境中能够提供最佳响应。幸运的是,有几种可用的工具可以帮助简化该过程,使您能够更高效地扩展应用程序。
One of the most popular tools among LLM developers is the LLM agent. This tool assists users in generating responses quickly by creating a sequence of related prompts and answers in a logical order. LLM agents leverage the power of LLMs to determine which actions to take based on the user’s initial prompt. They utilize different tools that are designed to perform tasks such as searching a website or extracting information from a database to provide a comprehensive and detailed response for the user. Essentially, agents combine LLMs with prompt templates to create a series of prompt-response pairs that ultimately provide the user with a final answer.
LLM开发人员中最受欢迎的工具之一是LLM代理。这个工具通过按照逻辑顺序创建一系列相关的提示和答案,帮助用户快速生成回应。LLM代理利用LLM的强大能力,根据用户最初的提示来确定下一步操作。它们利用不同的工具,如搜索网站或从数据库中提取信息,为用户提供全面和详细的响应。实质上,代理将LLM与提示模板结合起来,创建一系列的提示-响应对,最终为用户提供最终答案。
Agents can act as a blend of experts, drawing context-specific data from various sources and utilizing the appropriate prompt templates to find the most valuable information for the user. One of the most prominent examples of LLM agents is LangChain, which commonly employs the concept of retrieval augmented generation. This approach involves using chunks of documents to identify the most relevant information that will answer a user’s query. A diagram of an LLM agent architecture is provided below:
代理可以充当专家的综合体,从各种来源获取特定上下文的数据,并利用适当的提示模板找到最有价值的信息提供给用户。LLM代理的最著名例子之一是LangChain,它通常采用了检索增强生成的概念。这种方法使用文档的片段来识别最相关的信息,以回答用户的查询。以下是LLM代理架构的示意图:
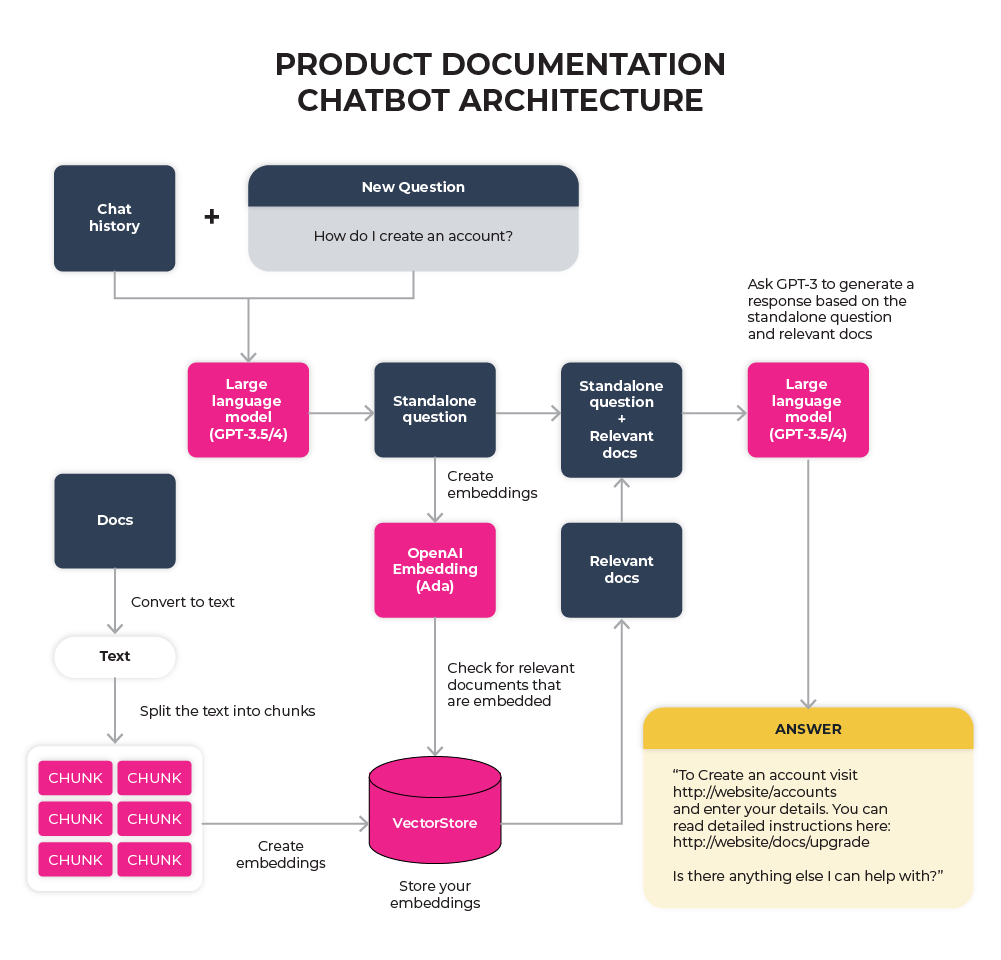
Example of an LLM agent architecture for a product documentation chatbot
产品文档聊天机器人的 LLM 代理体系结构示例
What Is LLM Observability?
什么是LLM可观测性?
As mentioned, what many machine learning teams are trying to achieve might be accomplished with a chain of prompts or agents in the future. So just like traditional machine learning observability, LLM observability is a must for deploying any LLM application at scale.
如前所提,未来许多机器学习团队试图实现的目标可能会通过一系列提示或代理的方式来实现。因此,与传统机器学习可观察性类似,在大规模部署任何LLM应用程序时,LLM的可观察性是必不可少的。
LLM observability is a tool for making sure that all the prompt templates, prompts, and responses are monitored in real time and prompt engineers can easily understand and find the root cause of any negative feedback and improve their prompts.
LLM可观测性是一种工具,用于确保实时监控所有提示模板、提示和响应,并使提示工程师能够轻松理解和找到任何负面反馈的根本原因,并改进其提示。
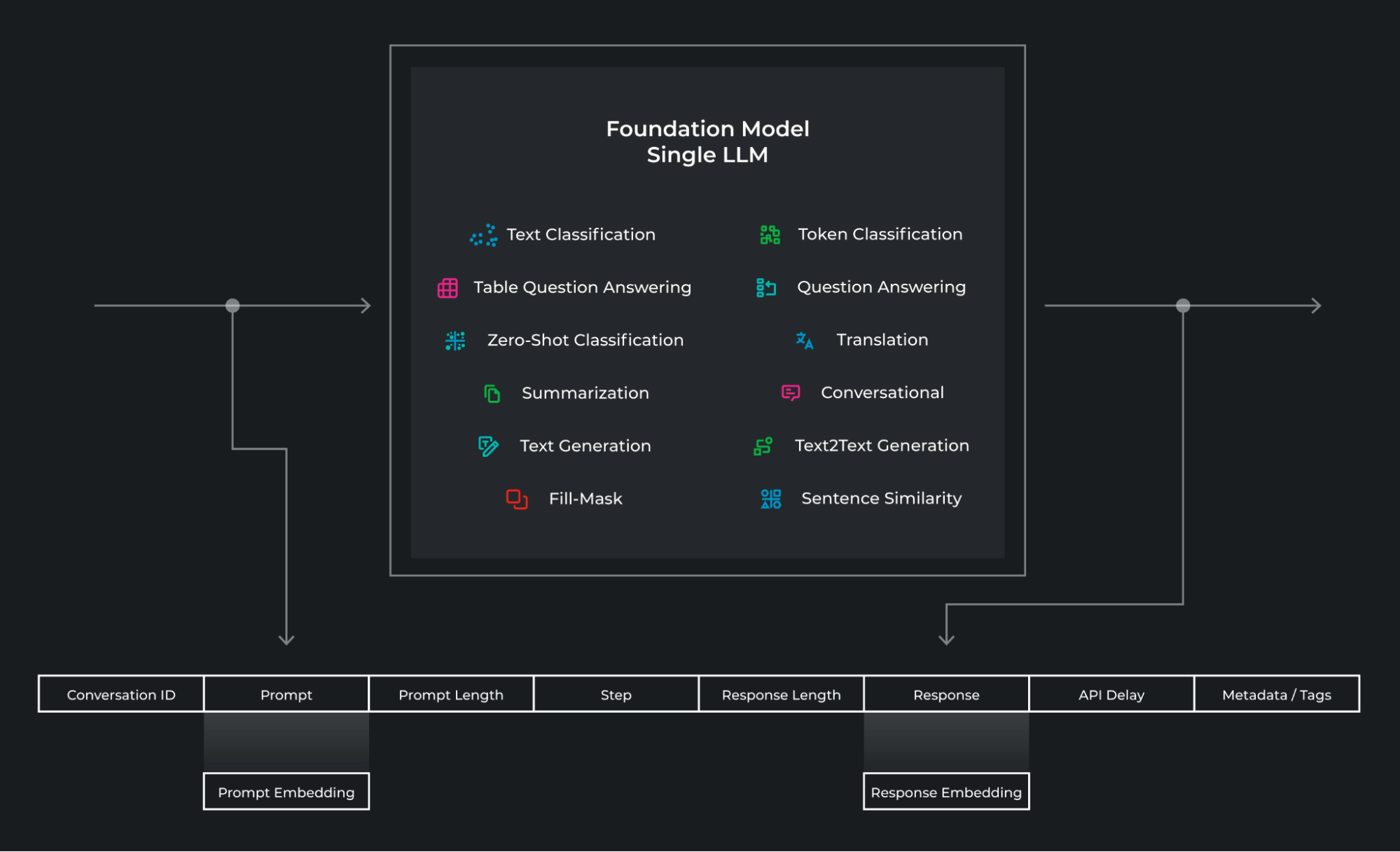
What Data Is Collected By An LLM Observability System? LLM可观测性系统收集哪些数据?
The above diagram shows what LLM observability looks like in the world of foundational models. The interface into and out of the system are strings of prompt/response pairs. The inputs and outputs are construct a set of data that is collected by the observability system that include the following:
以上的图表展示了在基础模型中,LLM的可观测性是如何运作的。系统的输入和输出是一系列的提示/响应对。通过这些输入和输出,LLM可观测性系统收集了以下数据:
- Prompt and response
- Prompt and response embedding
- Prompt templates
- Prompt token length
- Step in conversation
- Conservation ID
- Response token length
- Structured metadata, tagging groups of predictions
Embedded metadata, additional metadata that is embedded
- 提示和响应(Prompt and Response)
- 提示和响应嵌入(Prompt and Response Embedding)
- 提示模板(Prompt Templates)
- 提示令牌长度(Prompt Token Length)
- 对话中的步骤(Step in Conversation)
- 对话ID(Conversation ID)
- 响应令牌长度(Response Token Length)
- 结构化元数据,用于标记一组预测结果
- 嵌入式元数据,附加嵌入的元数据
Embeddings 嵌入
Embeddings are internal latent representations of information where they are an internal representation of what a model is “thinking” and how it sees that specific data. In a foundational model like GPT-4, teams do not have access to the internal embeddings for that specific model but can still generate embeddings using an embedding generator model. The embedding generator models can be locally run models such as GPT-J or BERT.
嵌入(Embeddings)是信息的内部潜在表示,它们是模型“思考”和观察特定数据的内部表达方式。在像GPT-4这样的基础模型中,团队无法访问该特定模型的内部嵌入,但仍可以使用嵌入生成模型生成嵌入。嵌入生成模型可以是本地运行的模型,例如GPT-J或BERT。
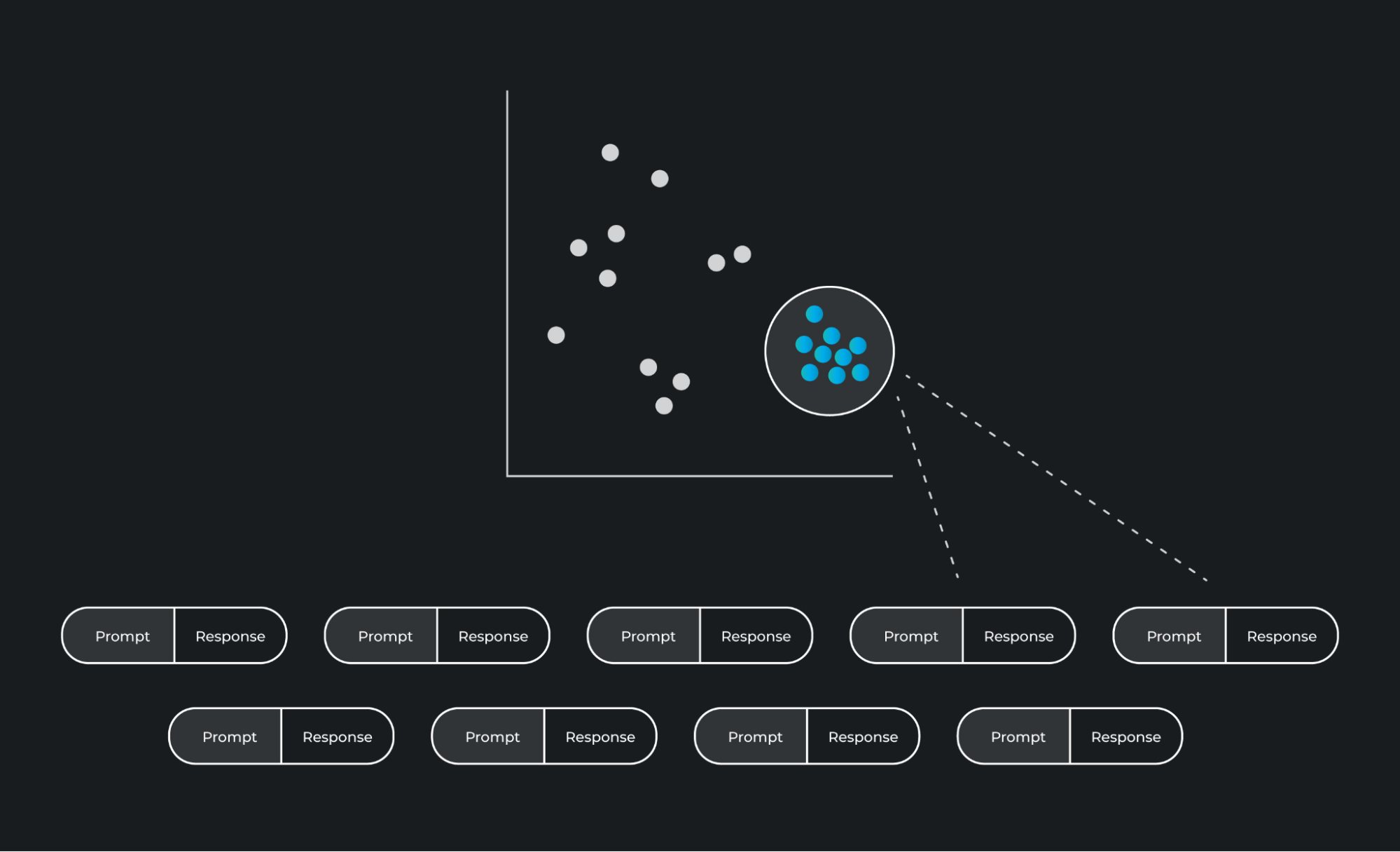
These embeddings can then be monitored in real-time across high-dimensional space and any change in behavior or any negative feedback from users can indicate a problem within the LLM application. One method of finding problem responses involves clustering prompts and responses then finding problem clusters through looking at evaluation metrics per cluster, drift per cluster or user feedback – such as thumbs up / thumbs down – per cluster.
这些嵌入向量可以在高维空间中进行实时监测,从而可以检测LLM应用程序中的行为变化或用户的负面反馈,从而指示可能存在的问题。其中一种发现问题响应的方法涉及对提示和响应进行聚类,然后通过观察每个聚类的评估指标、漂移情况或每个聚类的用户反馈(例如赞/踩)来找出问题聚类。
Troubleshooting Workflow and Example
故障排除工作流和示例
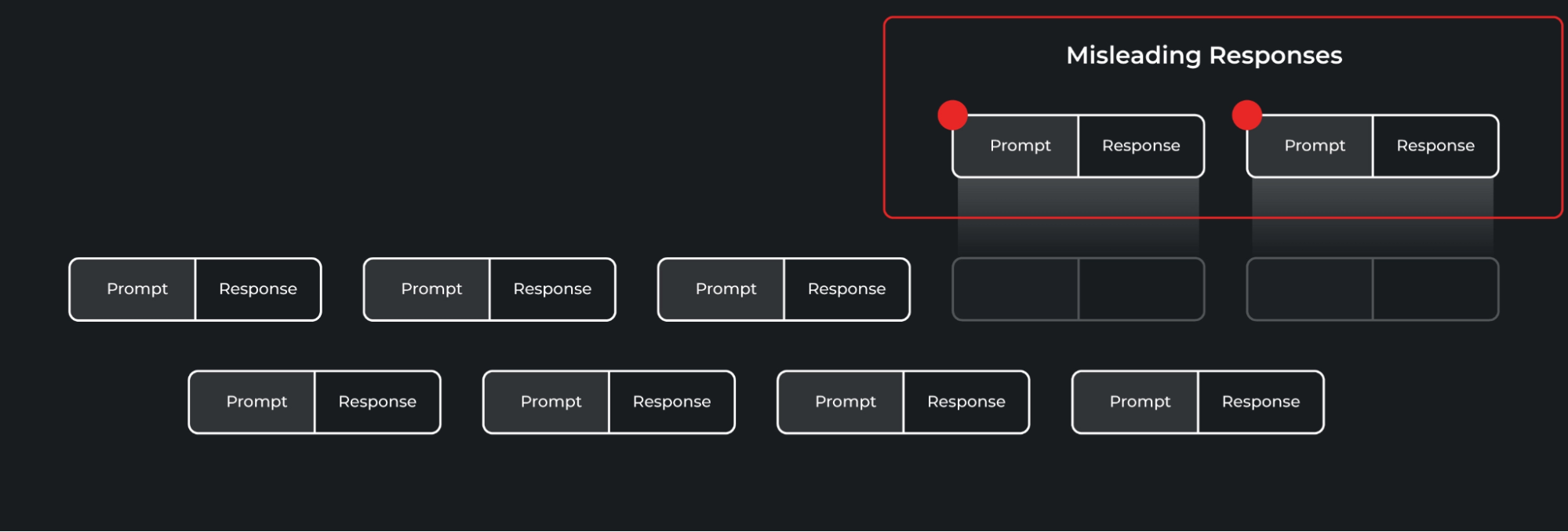
The problems captured as part of the detections are shown above, where a certain format of misleading responses are grouped together and highlighted. These misleading responses can be fixed through a number of iterative workflows through prompt engineering or fine-tuning.
上面展示了检测结果中捕获的问题,一些具有误导性的回应按照特定的格式被分组和突出显示。通过一些迭代的工作流程,可以通过提示工程或微调来修复这些具有误导性的回应。
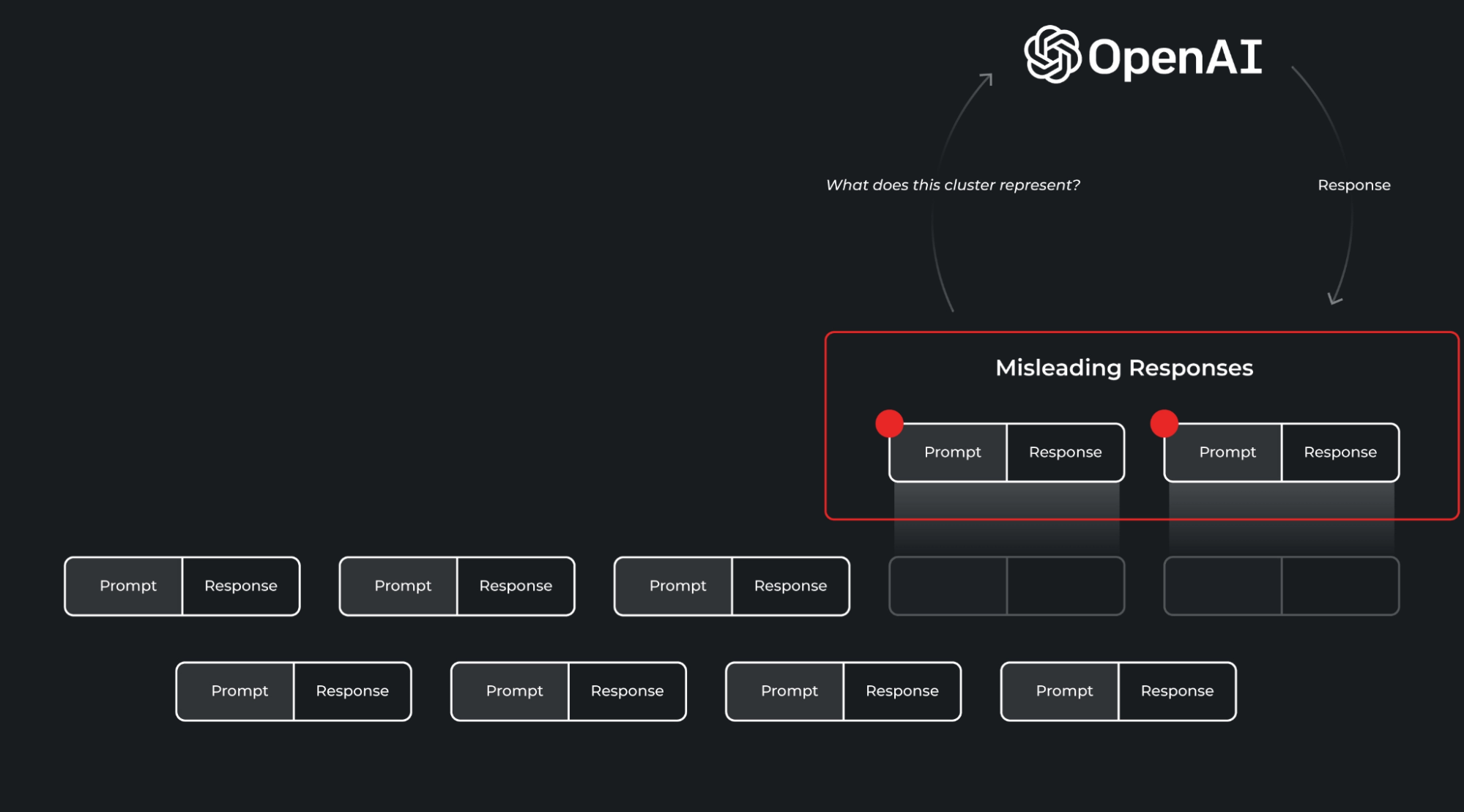
Once you find a cluster of issues, understanding what specifically in that cluster is problematic can take some work. We recommend integrating an LLM to do the heavy lifting for you. Your LLM observability tool should have a prompt template for the LLM with cluster data to do cluster analysis and cluster comparisons to baseline datasets, with interactive workflows for EDA-type analysis.
一旦发现了问题集群,理解在该集群中具体存在什么问题可能需要一些工作。我们建议集成LLM以为您进行大部分工作。您的LLM可观测性工具应该针对LLM设置提供一个提示模板,用于进行集群分析和与基准数据集进行对比,同时提供交互式EDA类型分析的工作流程。这样可以帮助您更好地了解集群中存在的问题。
In addition to cluster analysis on the full datastream, many teams want observability solutions to segment their data on structured data related to the prompt and response pairs. This metadata can be API latency information, enabling teams to look laser in on the prompt/response pairs causing a large latency before zooming into clusters. Or they can dig in based on structured metadata provided by the production integration. These can be related to pre-prompt task categories or any metadata relevant to the prediction.
除了对完整数据流进行集群分析外,许多团队希望可观测性解决方案可以根据与提示和响应对相关的结构化数据对其数据进行分段。这些元数据可以是API延迟信息,使团队能够专注于导致大延迟的提示/响应对,然后再进一步聚焦于集群。或者他们可以根据生产集成提供的结构化元数据进行深入挖掘。这些元数据可以与提示之前的任务类别相关,或者与预测相关的任何元数据有关。
Conclusion 结论
In conclusion, the rapid growth of large language models in various applications has necessitated the development of effective operational strategies and the relatively new discipline of LLMOps to ensure these models perform optimally in production environments. Key components of LLMOps include prompt engineering and management, LLM agents, and LLM observability. By employing these techniques, developers can optimize their LLMs to handle specific tasks, efficiently manage prompts, and monitor model performance in real-time. As the adoption of LLMs continues to expand, LLM observability allows for fine-tuning and iterative prompt engineering workflows. By identifying problematic clusters of responses, developers can refine their prompt engineering techniques or fine-tune the model to enhance its performance. This iterative process ensures continuous improvement of the LLM application, leading to a better end-user experience.
总结起来,大型语言模型在各种应用中的快速增长要求开发出有效的运营策略,并且相对较新的LLMOps学科的发展,以确保这些模型在生产环境中发挥最佳性能。LLMOps的关键组成部分包括提示工程和管理、LLM代理和LLM可观测性。通过采用这些技术,开发人员可以优化LLM以处理特定任务,有效管理提示,并实时监测模型性能。随着LLM的不断推广,LLM可观测性允许进行微调和迭代的提示工程工作流程。通过识别问题响应的集群,开发人员可以改进其提示工程技术或微调模型以提升性能。这个迭代过程确保了LLM应用程序的持续改进,从而提供更好的最终用户体验。
文档信息
- 本文作者:王翊仰
- 本文链接:https://www.wangyiyang.cc/2023/08/30/llmops-operationalizing-llms-at-scale/
- 版权声明:自由转载-非商用-非衍生-保持署名(创意共享3.0许可证)
